Publishing to Connect using Jenkins CI/CD
Overview of Deploying to Connect
Connect hosts a variety of data artifacts with different development life-cycles. Whenever you want to publish one of these data artifacts to Connect, there are three paths you can follow:
- Hands-on deployment process from within a development environment
- Git-backed deployment within Connect
- Programmatic deployment
This page focuses on the third option, programmatic deployment using Jenkins as a continuous integration and deployment pipeline. Continuous integration (CI) is the practice of automating the integration of code changes. That automation can entail running different tests or other pre-deployment activities. Continuous deployment (CD) is the practice of automating the deployment of code changes to a test or production environment. Many popular code hosting providers and independent software companies offer CI and CD services. These pipelines allow you to build for specific operating systems/environments, integrate tests and publish to Connect from private repositories without a service account.
The following section examines the deployment of a Shiny application to Connect using Jenkins.
Scope
Jenkins is a CI/CD server that is independent of a git server. Therefore, a variety of different hosting services (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, Azure Repos) can be used with Jenkins. This article provides two examples showing how to integrate Jenkins with git repositories hosted on GitHub and Azure Repos.
Demo GitHub Repository: https://github.com/sol-eng/shiny-app-demo-cicd-jenkins
Demo Azure Repos Repository: https://dev.azure.com/trevornederlof/_git/shiny-app-demo-cicd-jenkins
The focus of this work is on integration with popular git repository services. For full documentation on configuring and using Jenkins, refer to the official Jenkins documentation. Additionally, a more detailed review and tutorial specific to Connect deployments is available in this article: Connect Deployments with GitHub Webhooks and Jenkins
Configuring Your Git Repository
To deploy via Jenkins, your git repository hosting service must be set up to push each time a specific event occurs in the repo, usually code being pushed to a specified branch. This process looks different depending on the git hosting service you are utilizing.
GitHub Specific Setup
In the case of GitHub, navigate to the Settings page, then select Webhooks from the left sidebar. Add a new webhook to see the management form as shown here:
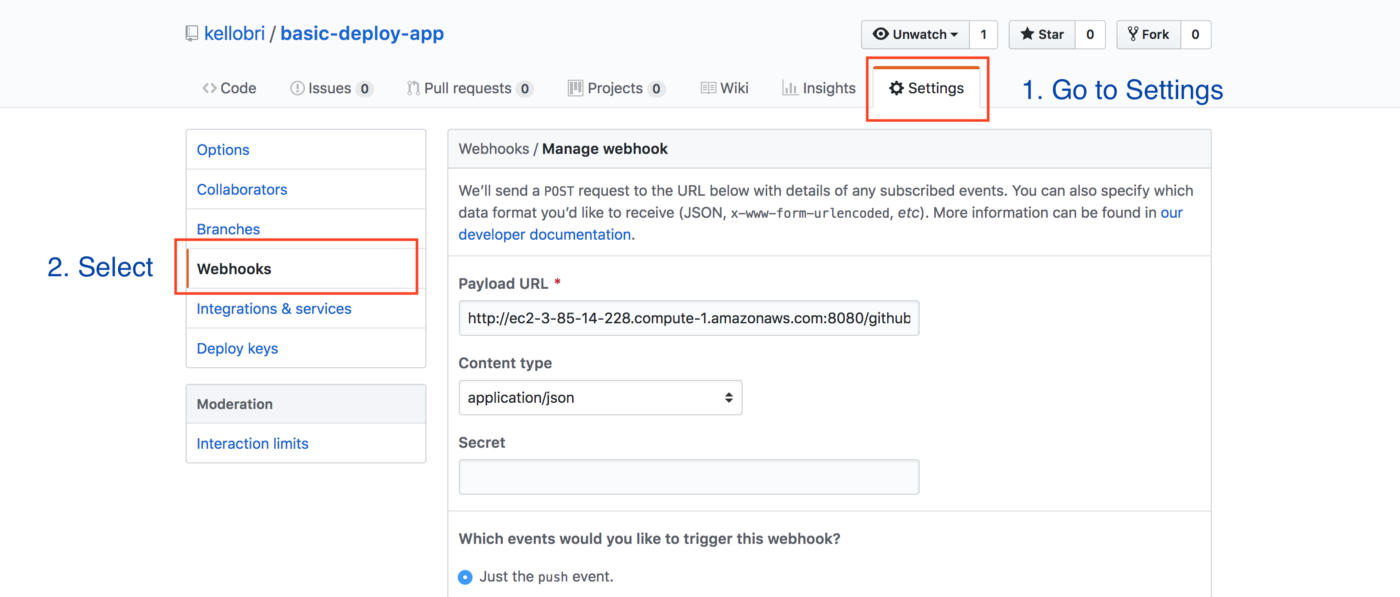
For the Payload URL field, provide the URL of your Jenkins server with /github-webhook/ appended to it. These are the selections to set for the webhook:
- Payload URL:
https://[JENKINS SERVER URL]/github-webhook/ - Content type: application/json
- Secret: [blank] - you can either leave this blank or utilize it depending on your Jenkins setup
- Event triggers: Just the push event
- Active: Check
On the Jenkins server, ensure the GitHub plugin is installed, the GitHub repository is set up in the configuration, and the GitHub hook trigger for GITScm polling is enabled.
Azure Repos Specific Setup
In the case of Azure Repos, navigate to the Project settings page, then select Service hooks from the left sidebar. Click Create subscription to see the form as shown here:
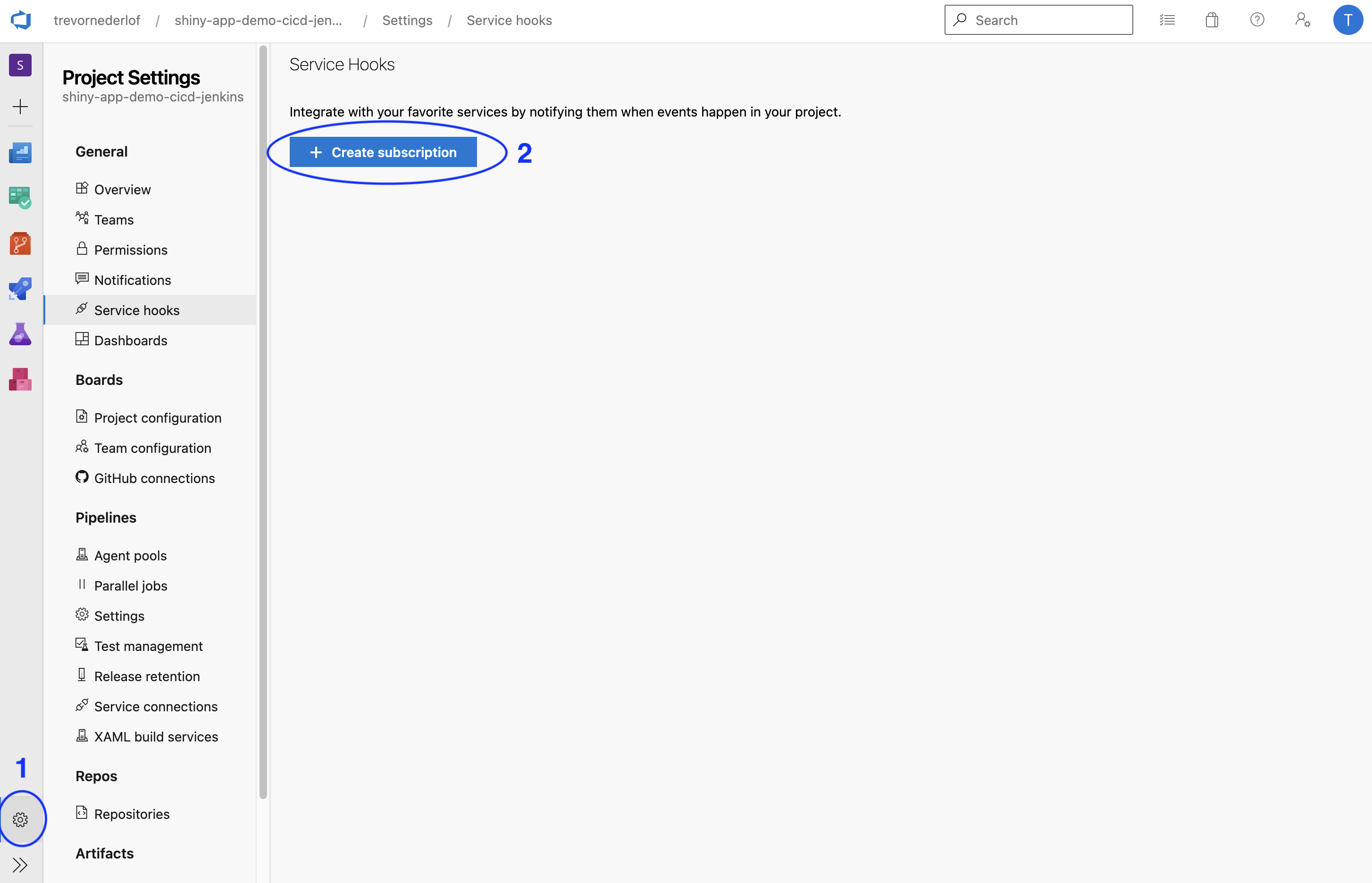
First select Jenkins as the service. On the next screen select Code pushed as the trigger event referencing a specific repository and branch. On the final menu leave Trigger generic build selected, enter in your Jenkins server URL with a username and API token. Before you leave this screen it is a good idea to test the connection with the Test button below. These are the selections to set for the service hook:
Trigger on this type of event: Code pushed
Repository: [REPO NAME SELECTED HERE]
Branch: [BRANCH SELECTED HERE]
Pushed by a member of group: your choice
Perform this action: Trigger generic build
Jenkins base URL:
https://[JENKINS SERVER URL]User name: [MY JENKINS USERNAME
User API token (or password): [MY JENKINS API TOKEN]
On the Jenkins server, ensure the Azure Repo URL is entered in the configuration. No plugin is needed beyond Git.
Configuring Jenkins to Deploy to Connect
A Jenkins server can be utilized in many different ways to run desired pre-deployment build and testing processes. After successful completion of these processes, you can utilize bash recipes to interface with the Connect API to deploy to Connect.
An example script to deploy content to Connect can be seen here: Deploy to Connect Script. Note this script requires the following environment variables to be configured in Jenkins:
CONNECT_SERVER: URL to the Connect Server
CONNECT_API_KEY: API key obtained from user settings in Connect
CONTENT_DIRECTORY: Directory where the actual content files are. In the example repository case it iscontent-dir.
After configuring your git repository and Jenkins server, pushes to your specified git branch will trigger a Jenkins CI/CD pipeline and deploy your content to Connect.